AC motors (Alternating Current motors) are motors that convert electrical energy into mechanical energy. They usually work with alternating current sources such as mains electricity. They are widely used in industrial and domestic applications.
The working principle of AC motors is based on the movement of a rotating rotor by the interaction of magnetic fields. The alternating current passing through the stator windings creates a rotating magnetic field. This magnetic field creates a force on the rotor and causes rotational motion.
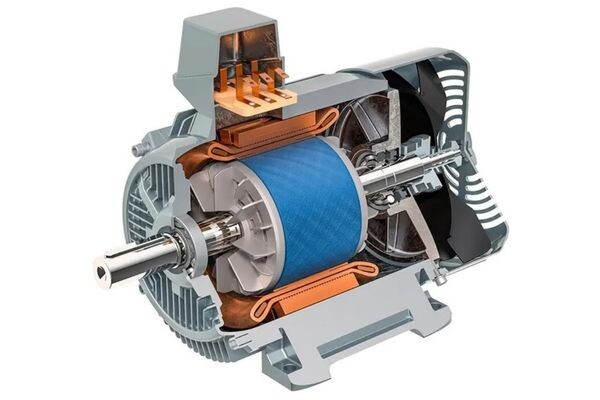
Stator: It is the part that produces the fixed magnetic field. It usually contains electromagnets.
Rotor: It is the rotating part. Contains short-circuited windings or permanent magnets.
Armature: Usually the windings of the rotor.
Bearings: Supports that allow the rotor to rotate smoothly.
Synchronous Motors:
The rotor speed is synchronized with the rotating magnetic field of the stator.
Usually used in applications requiring high precision.
Asynchronous (Induction) Motors:
The rotor speed is slightly lower than the rotating magnetic field of the stator.
Structurally simpler and more durable.
It is frequently used in daily life such as washing machines, fans, compressors.
Industrial machines and pump systems
Home appliances (refrigerators, washing machines)
HVAC systems (Heating, ventilation and air conditioning)
Electrical vehicles
Agricultural machinery
Low maintenance requirement
High efficiency
Reliability and long life
Speed control is difficult.
Power factor problems can be experienced.
AC motors are widely used in various industrial and daily applications. They continue to be used in various projects with their different types and advantages. They are frequently preferred especially in applications requiring high power.